LeetCode Top Interview Questions [Medium Collection]
Tree And Graph
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
-
완전 이진 트리가 주어질 경우에 내부의 next가 오른쪽의 노드를 가르키게 하는 것.
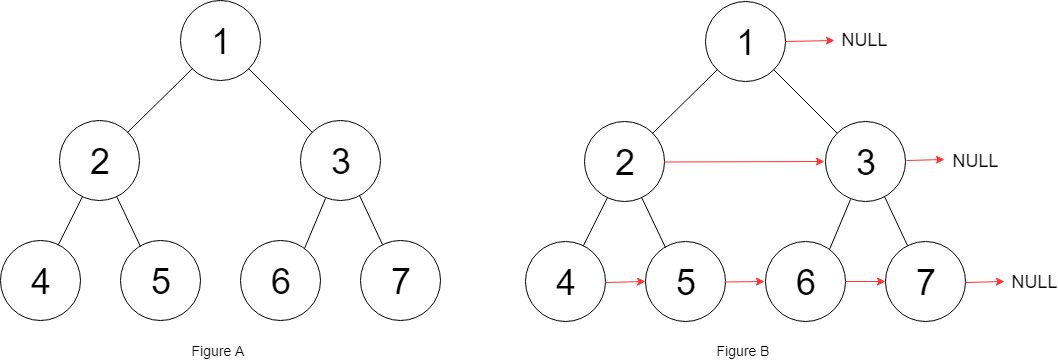
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]- root노드를 받아 queue에 넣는다.
-
depth가 변경 될 때마다. size를 캐싱한다.
ex)
depth = 2일 경우에 size = 2
depth = 3일 경우에 size = 4
- 2에서 캐싱한 size만큼, for문을 돌면서 이전 노드와 다음 노드를 연결하고, 이전 노드를 갱신한다.
- 캐싱한 size만큼 queue에서 꺼내고, 이전노드가 있다면 현재 노드와 연결한다.
- 연결한 이후에 해당 노드의 좌, 우 노드를 꺼내서 queue에 넣는다.
- 이전 노드를 현재 노드로 갱신 한다.
class Solution { public: Node *connect(Node *root) { queue<Node *> q; if (root == nullptr) { return nullptr; } q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { Node *Pre = nullptr; int tempSize = q.size(); for (int i = 0; i < tempSize; i++) { Node *now = q.front(); q.pop(); if (Pre != nullptr) { Pre->next = now; } if (now->left) q.push(now->left); if (now->right) q.push(now->right); Pre = now; } } return root; } };
Kth Smallest Element in a BST
- 이진 트리에서 n번째로 작은 노드를 출력하는 코드 그냥 전채를 코드에 넣고 가장 작은 값을 출력하는 코드 작성
class Solution
{
public:
int kthSmallest(TreeNode *root, int k)
{
vector<int> v;
queue<TreeNode *> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
TreeNode *curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if (curr == nullptr)
{
continue;
}
v.push_back(curr->val);
q.push(curr->left);
q.push(curr->right);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
return v[k - 1];
}
};
이진 트리이므로 이미 정렬되게 할 수 있을까..?
- stack생성 (선입 선출)
- 왼쪽의 끝까지 간다. (가장 작은 값)
- 이후 하나씩 꺼내면서 count++
- 오른쪽 서브 노드를 방문
- 2,3반복
class Solution {
public:
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* curr = root;
int count = 0;
while (curr != nullptr || !st.empty()) {
while (curr != nullptr) {
st.push(curr);
curr = curr->left;
}
curr = st.top();
st.pop();
count++;
if (count == k) return curr->val;
curr = curr->right;
}
return -1; // k가 유효하지 않은 경우
}
};
Number of Islands
토마토 문제와 유사함.
- 전체 탐색을 하면서 섬이 있을 경우(
arr[i][j] == 1) 섬의 갯수를 추가하고 dfs실행 - dfs에서 상하 좌우를 0으로 만들어 방문 처리를 한다.
class Solution
{
void dfs(vector<vector<char>> &grid, int i, int j)
{
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid[0].size();
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= rows || j >= cols || grid[i][j] == '0')
return;
grid[i][j] = '0'; // 방문 처리
// 상, 하, 좌, 우 탐색
dfs(grid, i - 1, j);
dfs(grid, i + 1, j);
dfs(grid, i, j - 1);
dfs(grid, i, j + 1);
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>> &grid)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].size(); j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == '1')
{
dfs(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
PREVIOUS알고리즘 스터디 4주차
NEXT알고리즘 스터디 6주차