LeetCode Top Interview Questions [Medium Collection]
Array and Strings, Linked List
Count and Say
재귀 사용
일단 문제에서도 나온 것 처럼 재귀로 해결
// Runtime : 3ms 82.95%
// Memory : 10.1MB 36.45%
class Solution
{
public:
string countAndSay(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
{
return "1";
}
string s = countAndSay(n - 1);
string ans;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
int cnt = 1;
for (auto j = i + 1; j < s.length(); j++, i++, cnt++)
{
if (s[i] != s[j])
break;
}
ans += to_string(cnt) + s[i];
}
return ans;
}
};
템플릿 메타 프로그래밍
뭔가 예전에 배운 템플릿 메타 프로그래밍 사용 가능할 것 같았음!
- 컴파일 타임에 해결이 가능하지만…
- 하지만 구현이 복잡함
// Runtime : 0ms 100%
// Memory : 10.6MB 25.28%
// 평가 함수 작성
string say(const string &s)
{
string ans;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)s.length(); i++)
{
int cnt = 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < (int)s.length(); j++, i++, cnt++)
{
if (s[i] != s[j])
break;
}
ans += to_string(cnt) + s[i];
}
return ans;
}
// 템플릿 메타 프로그래밍 struct선언
template <int N>
struct CAS
{
static const string string;
};
// 계산 로직
template <int N>
const string CAS<N>::string = say(CAS<N - 1>::string);
// 종료 로직 (끝점)
template <>
const string CAS<1>::string = "1";
class Solution
{
static constexpr int MAX_N = 30;
// 테이블 생성
template <size_t... I>
static const vector<const string *> &table_impl(index_sequence<I...>)
{
static const vector<const string *> t = {&CAS<int(I + 1)>::string...};
return t;
}
string GetAnswer(int n)
{
return *table_impl(make_index_sequence<MAX_N>{})[n];
}
public:
string countAndSay(int n)
{
return GetAnswer(n - 1);
}
};
Add Two Numbers
각 노드의 합 계산
// Runtime : 0ms 100.00%
// Memory : 77MB 91.93%
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2)
{
ListNode *lr = l1, *ll = l2, *Head = nullptr, *next = nullptr;
bool carry = false;
while (lr || ll)
{
int sum = 0;
if (lr != nullptr)
{
sum += lr->val;
lr = lr->next;
}
if (ll != nullptr)
{
sum += ll->val;
ll = ll->next;
}
if (carry)
{
sum++;
carry = false;
}
if (sum >= 10)
{
sum -= 10;
carry = true;
}
ListNode *temp = new ListNode(sum);
if (Head == nullptr)
{
Head = temp;
next = temp;
}
else
{
next->next = temp;
next = temp;
}
}
if (carry)
{
next->next = new ListNode(1);
}
return Head;
}
};
더미 노드 사용
- 1번 풀이와 변함이 거의 없으나 dummy노드를 사용해서 head에 대한 분기를 없앨 수 있다.
// Runtime : 0ms 100%
// Memory : 77.1MB 44.56%
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2)
{
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(), *temp = dummy;
bool carry = false;
while (l1 || l2)
{
int sum = 0;
if (l1)
{
sum += l1->val;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if (l2)
{
sum += l2->val;
l2 = l2->next;
}
if (carry)
{
sum++;
carry = false;
}
if (sum >= 10)
{
carry = true;
sum -= 10;
}
temp->next = new ListNode(sum);
temp = temp->next;
}
if (carry)
{
temp->next = new ListNode(1);
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Odd Even Linked List
💡 짝수 노드를 홀수 노드 뒤에 이어 붙이는 문제
{1,2,3,4,5} ⇒ {1,3,5,2,4}
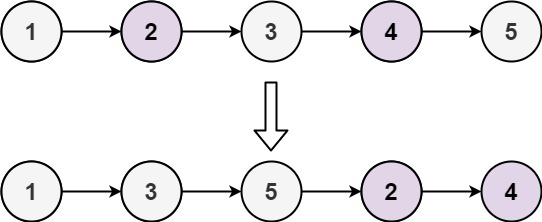
짝홀 리스틀 만들어 마지막에 이어주기
// Runtime : 0ms 100%
// Memory : 16MB ???%
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *oddEvenList(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *dummy1 = new ListNode(), *temp = dummy1;
ListNode *dummy2 = new ListNode(), *temp2 = dummy2;
bool even = false;
while (head != nullptr)
{
if (even)
{
temp->next = new ListNode(head->val);
temp = temp->next;
}
else
{
temp2->next = new ListNode(head->val);
temp2 = temp2->next;
}
even = !even;
head = head->next;
}
temp2->next = dummy1->next;
return dummy2->next;
}
};
Intersection of Two Linked Lists
💡 두개의 List중에 겹치는 부분을 출력 해주는 코드
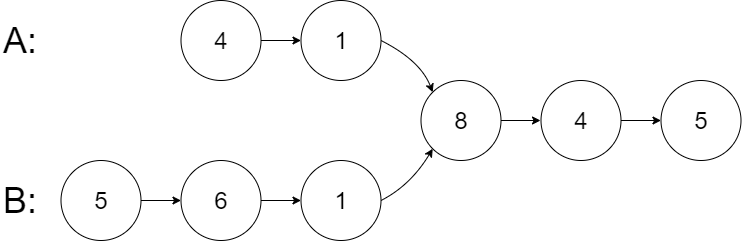
-
단 숫자가 같다고 겹치는게 아니라 노드의 주소까지 동일 해야 한다.
-
listA = [4,1,8,4,5],listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5]=>ans = [8,4,5]
unordered_set 사용
// Runtime : 54ms 11.77%
// Memory : 23.7MB 5.70%
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB)
{
unordered_set<ListNode *> set;
ListNode *temp = headA;
while (temp)
{
set.insert(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp)
{
if (set.find(temp) != set.end())
{
return temp;
}
set.insert(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
리스트 붙여서 확인
A와 B의 리스트가 있다면 Index를 맞춰서 해주는 방법.
A와 B를 붙여주면 길이가 같아지고,
두 리스트가 순회를 전부 마친다면 속도가 같아짐
A: A1 → A2 → A3→ X1→ X2 → null B: B1 → B2 → B3 → B4 → X1 → X2 → null
위와 같은 리스트가 있다면 두개를 이어 붙일 경우
A1 → A2 → A3→ X1 → X2 → B1 → B2 → B3 → B4 → X1 → X2→ null
B1 → B2 → B3 → B4 → X1 → X2→ A1 → A2 → A3 → X1 → X2→ null
이렇게 되어 끝이 맞춰지게 된다.
// Runtime : 54ms 11.77%
// Memory : 23.7MB 5.70%
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB)
{
ListNode *temp = headA;
ListNode *temp2 = headB;
while (temp != temp2)
{
temp = temp->next;
temp2 = temp2->next;
if (temp == temp2)
return temp;
if (!temp)
temp = headB;
if (!temp2)
temp2 = headA;
}
return temp;
}
};
PREVIOUS알고리즘 스터디 2주차
NEXT알고리즘 스터디 4주차