Word Search
m * n 의 보드와 문자열 word가 주어질 경우 해당 문자열이 있는지 확인하는 문제
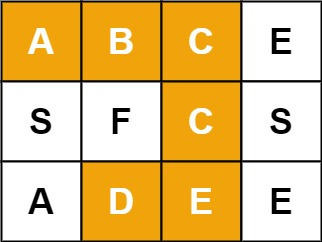
에서 ABCCED가 주어질 경우 위와 같다. ⇒ true
ABCCCBA는 C를 중복 사용해야해서 될 수 없다. ⇒ false
초기 구현
- map에 char을 기준으로 나오는 index를 기록
- set에 사용 유무 체크
- n * m 을 하나의 array로 정규화 (4*4라면 1~16)
- 문자열을 돌면서 좌우상하에 다음 문자열이 있는지 확인
- 단 좌우로 갈 경우 index가 다음 열인지 확인 해야 한다.
- 재귀를 통해 다시 확인
// 1665 ms 5.18%
// 148.8 MB 5.22%
class Solution {
unordered_map<char, vector<int>> map;
unordered_set<int> set;
int x = 0;
// 뒤부터 처리하는게 더 편한듯?
bool backtracking(string word, int index)
{
if (word.size() == 0)
{
return true;
}
char ch = word.back();
word.pop_back();
if (map[ch].size() == 0)
{
return false;
}
for (auto a : map[ch])
{
if (set.find(a) != set.end())
{
continue;
}
// 좌, 우, 상, 하
if (!(
(a == index + 1 && index / x == a / x) ||
(a == index - 1 && index / x == a / x) ||
(a == index + x) ||
(a == index - x)
))
continue;
set.emplace(a);
if (backtracking(word, a) == true)
{
return true;
}
set.erase(a);
}
return false;
}
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
int count = 0;
for (auto v : board)
{
for (auto item : v)
{
map[item].push_back(count++);
}
}
x = board[0].size();
char ch = word.back();
word.pop_back();
if (map[ch].size() == 0)
{
return false;
}
for (auto a : map[ch])
{
set.emplace(a);
if (backtracking(word, a))
{
return true;
}
set.erase(a);
}
return false;
}
};
근데 속도가 너무 느려서 개선
개선점
- map을 저장하지 않는 방법 생각 (board가 같은 문자열로 전부 채워질 경우 n^2이 되어 안좋을 것 같음)
- dfs를 통해 해결
- 문자열 (word) 복사 비용이 클것 같음
- 문자열을 ref로 복사한 뒤에, index만 따라간다.
// 471 ms 41.65%
// 11.6 MB 33.21%
class Solution {
vector<vector<bool>> visited;
bool dfs(const vector<vector<char>>& board, const string& word, int x, int y, int wordIndex)
{
if (wordIndex == word.size())
return true;
if (y < 0 || y >= board.size() || x < 0 || x >= board[0].size())
{
return false;
}
if (visited[y][x] || word[wordIndex] != board[y][x])
{
return false;
}
visited[y][x] = true;
if (dfs(board, word, x - 1, y, wordIndex + 1) ||
dfs(board, word, x + 1, y, wordIndex + 1) ||
dfs(board, word, x, y - 1, wordIndex + 1) ||
dfs(board, word, x, y + 1, wordIndex + 1))
return true;
visited[y][x] = false;
return false;
}
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
visited.assign(board.size(), vector<bool>(board[0].size(), false));
for (int y = 0; y < board.size(); y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < board[y].size(); x++)
{
if (dfs(board, word, x, y, 0))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
- 더 개선이 가능해 보이지만 일단 여기까지..
Sort Colors
3가지 색상으로 칠해진 객체로 구성된 배열을 정렬하는 문제
- quick sort사용 pivot와 대소 비교를 기준으로 좌우로 나눈 뒤에 분할 정복
// 0ms 100.00%
// 11.6MB 48.94%
class Solution {
void quicksort(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= end)
{
return;
}
int pivot = start;
int left = pivot + 1;
int right = end;
while (left <= right)
{
while (left <= end && nums[left] <= nums[pivot])
{
left++;
}
while (right > start && nums[right] >= nums[pivot])
{
right--;
}
if (left > right)
{
swap(nums[pivot], nums[right]);
}
else
{
swap(nums[left], nums[right]);
}
}
quicksort(nums, start, right - 1);
quicksort(nums, right + 1, end);
}
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums)
{
quicksort(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};
Top K Frequent Elements
num과 k가 주어질 경우에 num에서 자주 노출되는 원소 k개를 출력하는 문제
ex) nums = {1,1,1,2,2,3}, k = 2 일 경우 {1,2}
- map에 < num, 빈도 > 로 저장한다. (find를 빠르게 하기 위해 map사용)
- vector으로 변경 (정렬 하기 위해)
- 결과값을 k까지만 저장하여 리턴
// 0ms 100.00%
// 18.1MB 27.75%
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
for (auto a : nums)
{
map[a]++;
}
// map -> vector으로 변환
vector<pair<int, int>> v(map.begin(), map.end());
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) {
return a.second > b.second;
});
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
result.push_back(v[i].first);
return result;
}
};
PREVIOUS알고리즘 스터디 6주차